To open NSLOOKUP:
- Press and hold the Windows Key on your keyboard, then press R.
- In the RUN box that appears, type: cmd and press enter.
- On the command prompt, type: nslookup and press enter.
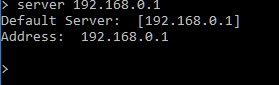
As you can see, the screen below is using the local Router (192.168.0.1) as the default server. This means any DNS records are coming from that server.
It can be handy to check DNS against other servers, to be sure your DNS server hasn't cached the records.
To change to another server, for example Googles Public DNS server, type:
server 8.8.8.8
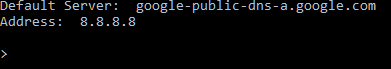
You can see the server is now showing as google-public-dns-a.google.com. Which basically means any queries you enter from here, will be how google "sees" things.
The beauty of NSLOOKUP is that you can query various DNS types, we have listed the main 4 you will use below:
CNAME - Canonical Name
MX - Mail Routing
NS - Name Servers
A - A records
To change the query type, you use the command: 'set q=[TYPE]' where type is one of the above 4 DNS record types. For example:
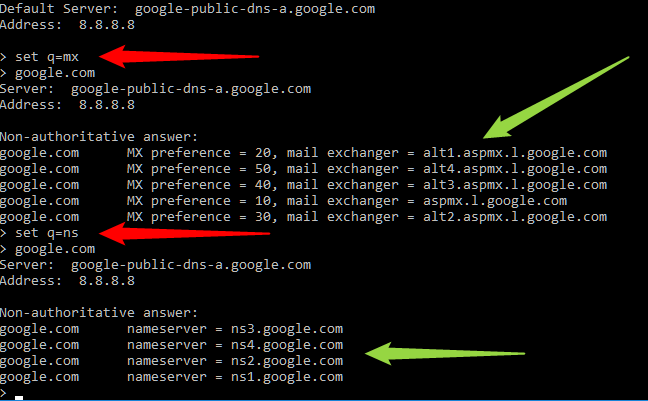
set q=mx
...will swap the query to Mail Records, or:
set q=ns
...will query the NameServers.
See examples of both below, Red arrows showign the change of Query type and the green showing the results.